Teachers and Students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
Measurement Traceability to the SI
Historical and International Aspects of the SI
20 May 1875
《米制公約》(法語:Convention du Mètre,英語:Metre Convention). The Convention was signed by representatives of seventeen nations. The Convention is an Inter-governmental diplomatic treaty on the matters of world metrology that created the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (法語:Bureau international des poids et mesures,縮寫:BIPM).
The Metre Convention was originally drawn up for units of length and mass only.
 Bureau international des poids et mesures
Bureau international des poids et mesures
In 1960
The full system and name "Système International d'Unités" (English: International System of Units - SI) were adopted at the 11th General Conference of Weights and Measures (CGPM). The SI is a set of rules that defines the unit of measurement of all quantities used in science and technology. It lays down rules for the base units, the derived units and prefixes.
There are seven SI base units.
| Time | second (s) | (Defined in 1967) |
| Length | metre (m) | (Defined in 1983) |
| Luminous Intensity | candela (cd) | (Defined in 1979) |
| Mass | kilogram (kg) | (Revised in 2019) |
| Electric Current | ampere (A) | (Revised in 2019) |
| Thermodynamic Temperature | kelvin (K) | (Revised in 2019) |
| Amount of substance | mole (mol) | (Revised in 2019) |
Metrology Infrastructure
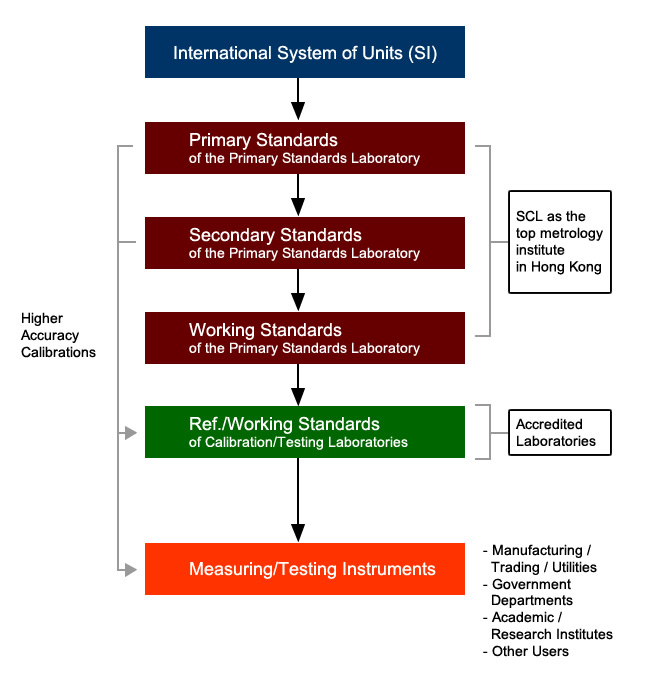 Metrology Infrastructure
Metrology Infrastructure