Triple Point of Water Cell
Primary Standard for Realization of the kelvin – Triple Point of Water Cell
 Photo of the SCL triple point of water cell
Photo of the SCL triple point of water cell
The kelvin is the SI base unit for thermodynamic temperature. The precise measurement of thermodynamic temperatures is difficult. Practical temperature scales were therefore introduced to make use of instruments such as platinum resistance thermometers which are easier to use and give more precise measurement results. The first International Temperature Scale was adopted in 1927, revised in 1948 as IPTS-48, revised again in 1968 as IPTS-68, and again in 1990 as the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90). Officially SCL adopted the ITS-90 from 1 January 1990.
Prior to 20 May 2019, the kelvin was defined as the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water. After 20 May 2019, the kelvin is defined by fixing the numerical value of the Boltzmann constant k to 1.380 649 x 10-23. This value was selected to ensure that the best estimate value of water triple point remains at 273.16 K. Hence the redefinition of the kelvin will not affect the readings of previously calibrated thermometers. The ITS-90 adopted by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) will continue to be the worldwide effective method for practical temperature measurement after the redefinition. SCL will continue to adopt the measurement standard in compliance with the ITS-90 to offer temperature calibration services traceable to the revised SI.
To realise the temperature using ITS-90, the "Guide to the Realization of the ITS-90" published by the Consultative Committees for Thermometry (CCT) should be followed. In addition to the triple point of water cells, SCL realises the ITS-90 by maintaining the following fixed point standards at :
- Triple point of argon (-189.3442°C).
- Triple point of mercury (-38.8344°C).
- Melting point of gallium (29.7646°C).
- Freezing point of indium (156.5985°C).
- Freezing point of tin (231.928°C).
- Freezing point of zinc (419.527°C).
- Freezing point of aluminium (660.323°C).
- Freezing point of silver (961.78°C).
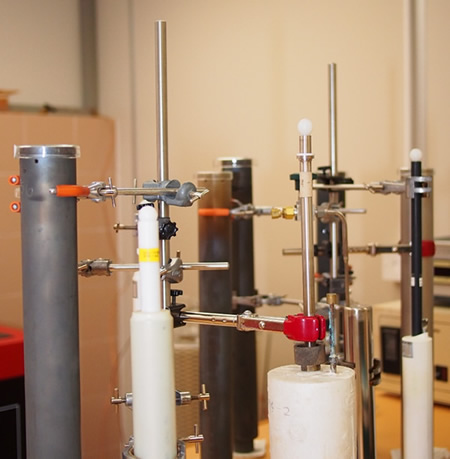 Some temperature fixed point standards of SCL
Some temperature fixed point standards of SCL
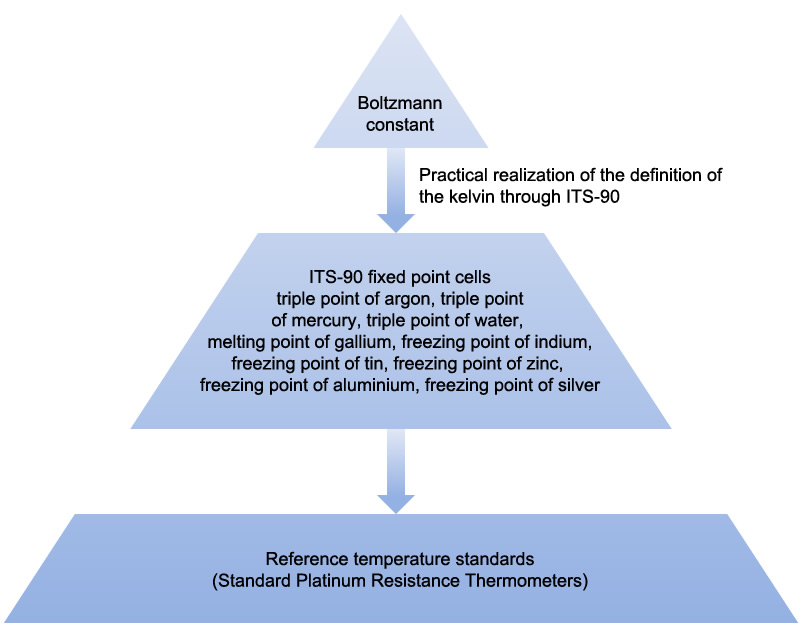 The traceability chain from the definition of the kelvin is illustrated in the following diagram.
The traceability chain from the definition of the kelvin is illustrated in the following diagram.
Reference
- Mise en pratique for the definition of the kelvin, prepared by the Consultative Committee for Thermometry (CCT).
- Guide to the Realization of the ITS-90, CCT, BIPM